Posts
VMware code execution flaw CVE-2021-21972
/in Cyber-security, Network Infrastructure, Network Security, News, Uncategorized/by Carl EasterdayThere is a newly disclosed code-execution vulnerability in VMware vCenter. VMware was quick to release a patch (within a day) and it can be found here.
The severity of this vulnerability as well as the fact that there are exploits available for both Windows and Linux servers, kicked off a flurry of mass scanning for vulnerable vCenter Servers.
Code execution, no authorization required
CVE-2021-21972 allows hacker with no authorization to upload files to vulnerable vCenter servers that are publicly accessible over port 443, researchers from security firm Tenable said. Successful exploits will result in hackers gaining unfettered remote code-execution privileges in the underlying operating system. The vulnerability stems from a lack of authentication in the vRealize Operations plugin, which is installed by default.
The flaw has received a severity score of 9.8 out of 10.0 on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System Version 3.0. Mikhail Klyuchnikov, the Positive Technologies researcher who discovered the vulnerability and privately reported it to VMware, compared the risk posed by CVE-2021-21972 to that of CVE-2019-19781, a critical vulnerability in the Citrix Application Delivery Controller
Ransomware and the impact to your business
/in Cyber-security, Network Security, News/by Carl EasterdayEveryday, you read another story about how a company has been hit by a ransomware attack, which potentially can disrupt your business, services to your clients and livelihood of your employees.
Just last week it was announced another company, Forward Air, was hit by a ransomware attack, which disrupted services and impacted revenue. This attack was attributed to a group “Hades”. Forward Air, a trucking company from Tennessee, posted revenues of $1.4 billion in 2019 and employs more than 4300.
The ransomware note, resembles a similar note used by another ransomware group known as “REvil”, also known as “Sodin”.
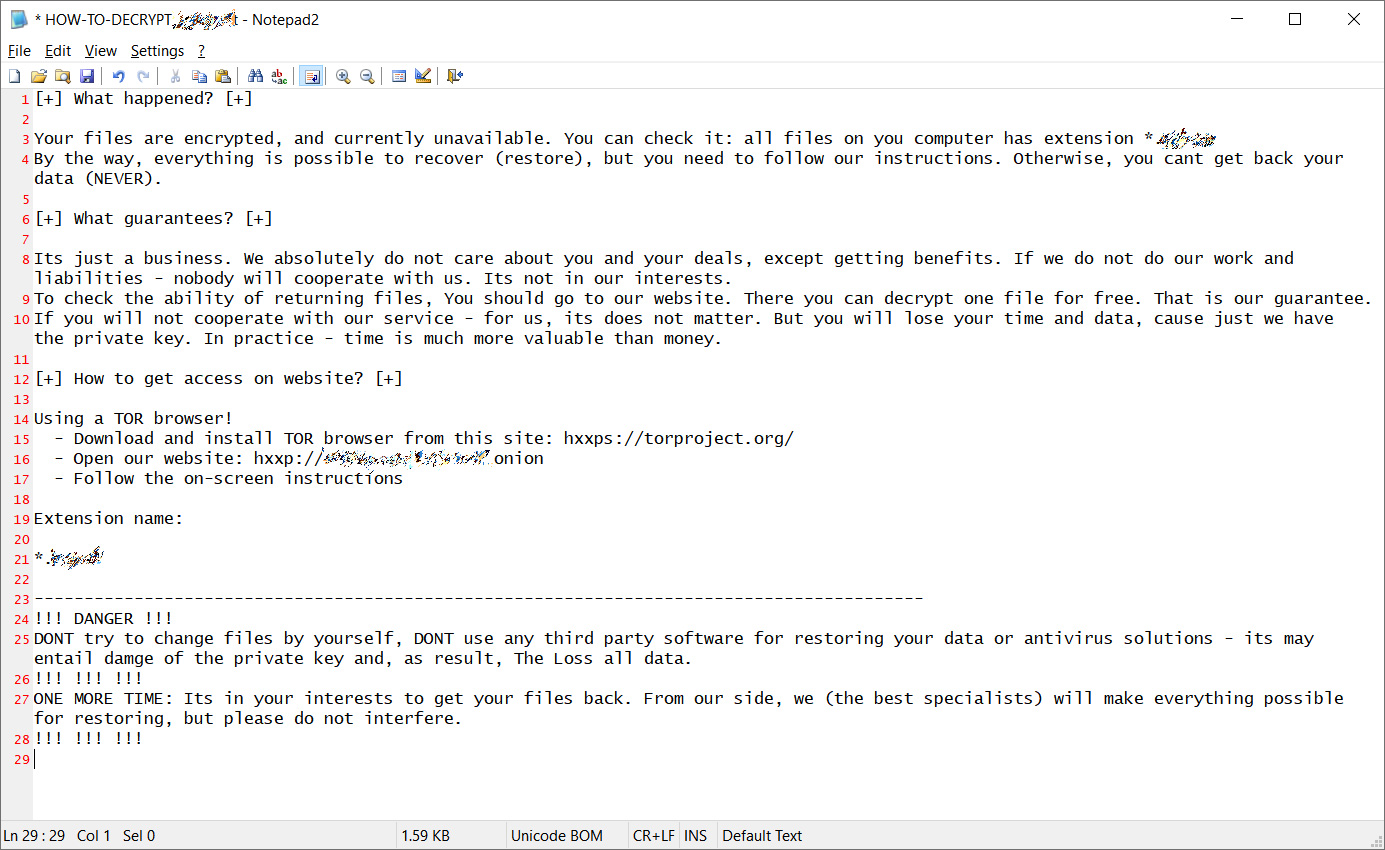
This is a Sodinokibi variant that was first seen in early 2019. Sodinokibi is what is known as ransomware-as-a-service, basically a software package which is catered by underground vendors to threat actors providing them a ransomware platform tool.
Companies are limited in their ability to defend against this type of exploitation, especially if they do not have full time IT staff or contracted Managed Service Providers that focus on security. Your organization must follow the following guidelines to help mitigate your exposure:
- Patch aggressively so vulnerabilities are eliminated and access routes are contained
- Enable endpoints with tools that automatically detect and respond to infections before they become systemwide
- Enable network threat intelligence tools to detect anomalies in your network traffic
- Make sure emails are screened for malicious payloads and links
- Minimize access levels by employees to perform their job functions
If you have been hit by ransomware, or just want to assess your company’s state of preparedness, reach out to us to discuss your needs.
LMJ is a full service Managed Service Provider, with offices in Alaska and California.
Cyber-security Training can save the day!
/in Computer Technology, Cyber-security, Network Security, Work from home/by Carl EasterdaySo you have secured your business.
Firewall, VPN for work from home, radius authenticated WiFi or perhaps an RDS gateway for remote desktops. Anti-virus is up to date, patching is top notch, SaaS applications locked up with two-factor authentication.
What about educating your workforce? Although Phishing is only the 5th most common primary cause of security incidents (per the Verizon 2020 Data Breach Report), following Denial-of-Service (DoS), data loss, Command and Control, or misdelivery of email/data – when it comes to data breaches Phishing is still number one.
Without a solid training plan for your employees, your business is at greater risk to have data compromised.
Top areas to look out for:
- Social Engineering
- Stolen Credentials
- Malware (usually delivered via email)
According to Verizon, Phishing is the first step in about 20% of security incidents and plays a role in another 30% of secondary steps to gain access to your information.
Highlights by Sector
Financial and Insurance:
- 1,509 incidents, 448 with confirmed data disclosure
- What did they target, Web Applications, Miscellaneous Errors and Everything Else
represent 81% of breaches - External to company (64%), Internal (35%), Partner (2%), Multiple (1%) (breaches)
- Financial motive (91%), Espionage (3%), Grudge (3%) (breaches)
- What did they get- Personal data (77%), Other (35%), Credentials (35%), Bank (32%)
(breaches) - How do they solve the problem -Implement a Security Awareness and Training Program (CSC 17),
Boundary Defense (CSC 12), Secure Configurations (CSC 5, CSC 11)

Healthcare:
- 798 incidents, 521 with confirmed data disclosure
- Miscellaneous Errors, Web Applications and Everything Else
represent 72% of breaches. - External (51%), Internal (48%), Partner (2%), Multiple (1%) (breaches)
- Financial motive (88%), Fun (4%), Convenience (3%) (breaches)
- What did they get – Personal data (77%), Medical (67%), Other (18%), Credentials (18%)
(breaches) - How do they solve the problem – Implement a Security Awareness and Training Program (CSC 17),
Boundary Defense (CSC 12), Data Protection (CSC 13)
But my company is too small for someone to try and get our data!
While differences between small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and large organizations remain, the movement toward the cloud and its myriad web-based tools, along with the continued rise of social attacks, has narrowed the dividing line between the two.
As SMBs have adjusted their business models, the criminals have
adapted their actions to keep in step and select the quickest and easiest path to their victims.
Contact us to get more information on our security practice and how you can have your team trained on cyber-security awareness.
Identity Management in the Cloud age
/in Cloud, Collaboration, Network Security/by Carl EasterdayYour business, like many companies, have adopted several cloud services, where the price and convenience outweighed the higher cost of hosting the application on your own servers. These services, be they email, documents, applications, databases or other collaboration tools, have broken the tightly guarded walled garden that your IT team has created behind your firewall and VPNs, allowing access to your company data via additional vectors with various security controls.
Most of these applications are only protected by one simple permission: the password.
Data breaches are becoming more and more commonplace. Lost and stolen data has exceeded six billion records in the past few year – an average of over 165,000 records compromised every hour! The related damage is estimated to exceed $6 Trillion annually by 2021. The recent Equifax breach, of a 143 million people (there are only 250 million or so adults in the US), highlights the vulnerability of weak passwords and open data portals.
In order to safeguard our important assets and reduce the risk of breaches, we need to rethink on how we approach organizational security
Access
New technologies, platforms and applications have accelerated the disintegration of the corporate security perimeter, creating a multitude of identities, user names and passwords. This use of cloud computing has increased trends of enabling employees to access network servers and sensitive information from outside the enterprise. Companies with static perimeter-based security methods (Firewalls, VPNS) will have a hard time managing both employee and partner access to critical data while maintaining any semblance of security.
Cyber criminals take aim at identities, from all types of users in your organization, from privileged users to vendors. They focus on weak passwords and social engineering to achieve their aims. Nearly two-thirds of all recently confirmed data breaches involved weak, default, or stolen passwords. In the first quarter of 2016 alone, there were an estimated 6.3 million phishing emails and 93% of all phishing emails contained ransomware.
Consequenses
No one is safe. In 2016, Yahoo revealed that the account information for over ONE BILLION consumers, including names, email addresses and encrypted passwords, were compromised by a data breach in 2013.
Dozens of companies experienced major outages when the DNS provider Dyn experienced a severe and extended Denial of Service attack (DDoS). What was the cause? Passwords. Default passwords on millions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices that were hijacked and used together as the Mirai botnet.
Next Stop, Security
How do we protect against breaches in our organizations, with this porous, multi-vendor, cloud-based enterprise? You must be able to adapt to new threats as they emerge. You must be able to incorporate cloud, mobile, IoT and other technologies, into a seamless defense, following your users as they work across applications and tools – Wherever they are hosted.
Companies must adopt Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions and practices that significantly reduce the likelihood of a data breach, by enabling secure access to your data from any device, for users inside and outside your organization.
How do we do this?
- Consolidate identify stores into a single directory
- Implementing single sign-on
- Governing access through time-bound and temporary privileged access
- Automating mobile application provisioning and deprovisioning of applications
- Automatically deprovision privileged user access as they terminate from your organization
- Eliminating the use of shared administrative accounts and centrally controlling access to shared service accounts
- Recording all privileged sessions or commands
- Automating role-based provisioning of applications and infrastructure
Forte can help your company ensure that identities are protected through an integrated solution across applications, devices and infrastructure.